Radiobotics: what is augmented intelligence?
More than 800 million medical images are being taken in Europe and the US combined, a number that is growing day by day while the number of qualified clinicians is dramatically decreasing.
A heavy workload at the radiology departments can lead to delays, errors, stress and and burnout among radiologists, and so Radiobotics was founded in September 2017 to solve this problem. Their vision is to build "augmented" healthcare technology that fully automates routine musculoskeletal x-ray readings, accelerated by state-of-the-art machine learning methods. "There are not enough radiologists to cope with the ever-growing number of medical images which leads to delay in diagnosis and treatment" explains Chief Operating Officer Stine Mølgaard Sørensen.
"This cannot be solved by educating more radiologists and clinicians, it simply takes too long. In fact, it takes more than 8 years to become a specialised radiologist" Sørensen says. "AI technology can play a crucial role and would basically give radiologists superpowers enabling them to make faster and more accurate decisions benefiting themselves, patients and the entire society. Hopefully, in 2-3 years we're at a stage where AI technology is indeed being implemented and used widely."
The company describes the technology radiobotics uses as augmented intelligence, rather than artificial intelligence. "We wish to give the radiologist extra capabilities by contributing to their workflow with technology that fully supports the x-ray readings. We don't believe in replacing radiologists with something artificial. We believe that everyone will win if our technology can make them better, faster and more consistent at what they already do."
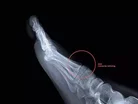
"Radiobotics has developed clinical validated algorithms that automates the analysis of routine x-ray images through image overlays and fully automated text reports. This AI-technology can help overloaded hospitals and give the clinicians and radiologists more time to spent with the patients. This being important because there's a global shortage of radiologists while the number of images of bones and joints is rapidly increasing. "
Radiobotics is still at an early stage but has already won the Danish Chamber of Commerce Award, several tech awards and a nomination for the Future Unicorn Awards 2021 as one of Europe's most promising scale-ups. Meanwhile in the US, Radiobotics has been selected for the Texas Medical Center’s accelerator program 2020.
Sørensen explains that Radiobotics' focus is on low-risk cases where they identify diseases in bones and joints. "This places us in a unique spot looking at the competitive landscape and other AI tools - the most focus is on other modalities like CT & MRI and high-risk pathologies like cancer and stroke detection.
"By automating the analysis of low-risk cases we position ourselves in an overlooked area where we are freeing up doctors’ time so they can spend it on more critical cases where they’re needed the most. Some might find it much more prestigious to solve problems within cancer, but we believe technology should initially solve the tedious and easy problems and while we build trust in technology, the radiologists should spend their valuable time on more complex and urgent cases."
"We see our focus as an overlooked ‘unsexy’ niche with a massive potential. Our internally developed tools/libraries and proprietary databases will allow much faster development and re-adaptation of algorithms for new musculoskeletal diagnosis applications. This will make us first mover in offering a fully automatic software for standardised analysis and reporting with much wider applicability than competitors."
